Overview
PoseGAN is a GAN-based architecture for generating realistic images of people conditioned on new poses. It uses two separate encoders to extract appearance and pose features, deforms source features to align with the target pose, and employs a decoder to synthesize the output image. A discriminator network ensures the generated image is realistic and preserves the person’s identity. The approach combines perceptual, nearest neighbour, and smoothness losses to maintain fine details and spatial coherence, enabling high-quality pose-driven image synthesis

Approach
- We started by learning the basic concepts of Neural Networks and Machine Learning.
- Using this knowledge, we implemented a handwritten digit recognition model (MNIST dataset) using simple 1- and 2-layer Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) with NumPy from scratch.
- We learned the basic concepts of optimizers, hyperparameter tuning, and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), and studied various architectures.
- Then, we implemented the MNIST model using the PyTorch framework — first with a 2-layer ANN and then with a deep CNN architecture.
- We further implemented an object detection model using the CIFAR-10 dataset with a deep CNN architecture, including batch normalization and dropout regularization.
- Next, we implemented Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to generate digits on the MNIST dataset, and later extended it to Conditional GANs (cGANs) on the same dataset.
- Finally, we implemented the Pose-based Human Image Generation architecture in PyTorch for the Market-1501 dataset, taking reference from a Research Paper by Siarohin et al.
Custom Dataset – MarketPoseDataset
This project includes a custom PyTorch dataset class called MarketPoseDataset, designed for pose-guided image generation. The dataset follows a structure where each pair consists of images of the same person in different poses, along with their corresponding pose maps. Each dataset item returns a dictionary containing:
- Source image
- Target image
- Source pose map
- Target pose map
We extract 18 human joint keypoints from each image and use YOLO-based pose estimation to generate corresponding heatmaps. These heatmaps are then converted into tensors for training. Pairing We use the Market-1501 dataset from Kaggle.
Model Architecture
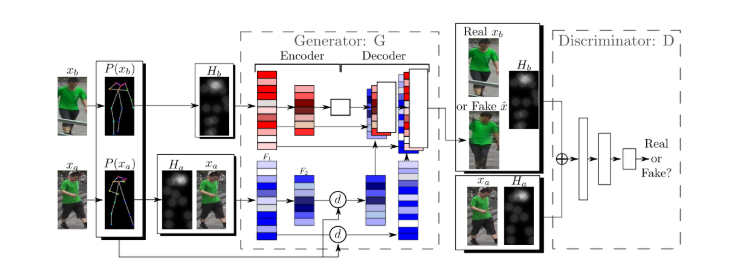
- Generator :- The DeformableGenerator is designed for pose-guided person image synthesis. It takes a source image and its pose map, along with a target pose map, and generates a new image of the person in the target pose.
- Architecture :- The generator follows an encoder–decoder structure with deformable skip connections that help align features between different poses.
- The encoder takes two inputs at a time: Source image (Xa) and its pose heatmap (Ha), Target pose heatmap (Hb) Low-level convolutional layers cannot effectively process both texture-level information (from Xa) and pose-level information (from Hb) simultaneously. Hence we use two separate encoders: The source encoder extracts appearance features from (Xa, Ha). The target encoder extracts pose features from Hb
- Source Encoder :- The source encoder takes the source image Xa and its pose heatmap Ha to extract appearance features. It learns a detailed visual representation of the person, including texture, color, and clothing.
- Target Encoder :- The target encoder takes only the target pose heatmap Hb to extract pose features. It learns a structural blueprint — where each body part should be — and guides the generator to reposition features accordingly.
- Deformable Warping :- After encoding, the source features are warped based on the difference between the source and target poses (Ha and Hb). This step aligns the appearance features to match the target pose.
- Warped Feature Fusion :- The warped features are aligned with the target pose and sent through deformable skip connections to the decoder.
- Decoder :- The decoder gradually upsamples and reconstructs the final image from the aligned features. It combines appearance and pose information to generate the output image. The final output is a generated image (x̂b) that resembles the real target image xb and matches the target pose Hb.
- Discriminator :- The discriminator (D) evaluates the realism of generated images. It receives two sets of inputs: Real pair: (xb, Hb), Fake pair: (x̂b, Hb), Source reference pair: (xa, Ha)
- Purpose :– The discriminator ensures: The generated image x̂b looks realistic. It correctly represents the same person as the source image xa. It matches the target pose Hb accurately.
Losses
There are two main types of losses: Generator Loss (L_G) and Discriminator Loss (L_D).
- Discriminator Loss (L_D) :- Measures how well the discriminator can distinguish between real and fake images. Its goal is to correctly identify real images as real and generated ones as fake.
- Generator Loss (L_G) :- Encourages the generator to produce realistic and well-aligned images that can fool the discriminator. It is composed of multiple sub-losses:
- Perceptual Loss :- Perceptual loss measures the difference between the generated image and the real target image, not at the pixel level, but in terms of high-level visual features. It helps the generated image look visually realistic and consistent with the real one. Fine details such as clothing texture, lighting, and shape are preserved, and it prevents blurriness that often happens with only pixel-level losses like L1 or L2.
- Nearest Neighbour Loss :- This loss preserves fine texture and structural details between source and generated images. It replaces common pixel-to-pixel losses (such as L1 or L2) and helps generate local information (like texture) similar to the target image, even when small spatial misalignments exist.
- Offset Smoothness Loss ;- Offset Smoothness Loss ensures that the deformable skip connections in the generator produce smooth and realistic spatial transformations when warping features from the source pose to the target pose. It keeps the warping smooth and continuous, prevents make this more shorter
Summary
- The source encoder captures visual appearance.
- The target encoder captures pose structure.
- Deformable warping aligns features between poses.
- The decoder reconstructs the final target-pose image.
- The discriminator ensures realism and identity consistency.
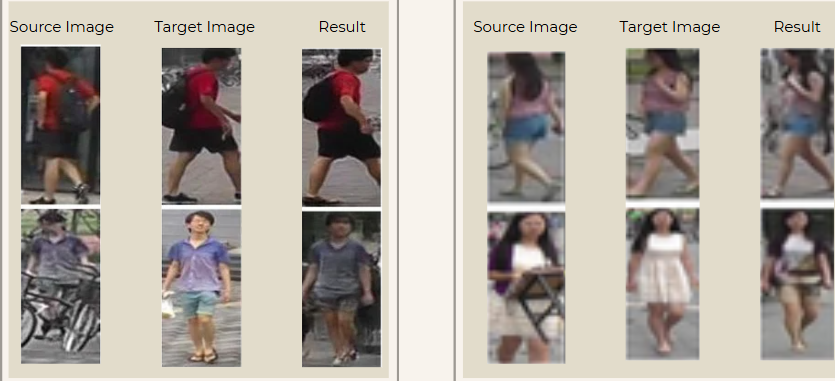
Results
Team Members
- Arya Baheti
- Ali Arhaan Ansari
- Kailash sankhla
- Navya Deshmukh
Mentors
- Shaan Vora
- Siddharth Hoonka
- Rohan Swain
- Arjun Jaishankar
- Srishti Singh
- Atharva Joshi