Overview
This project implements a Region Captioning System that bridges the gap between Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing using Deep Learning.
Unlike traditional image captioning models that describe an entire image with a single sentence, Region Captioning focuses on generating fine-grained, natural language descriptions for specific regions within an image, offering a more localized and contextual understanding.
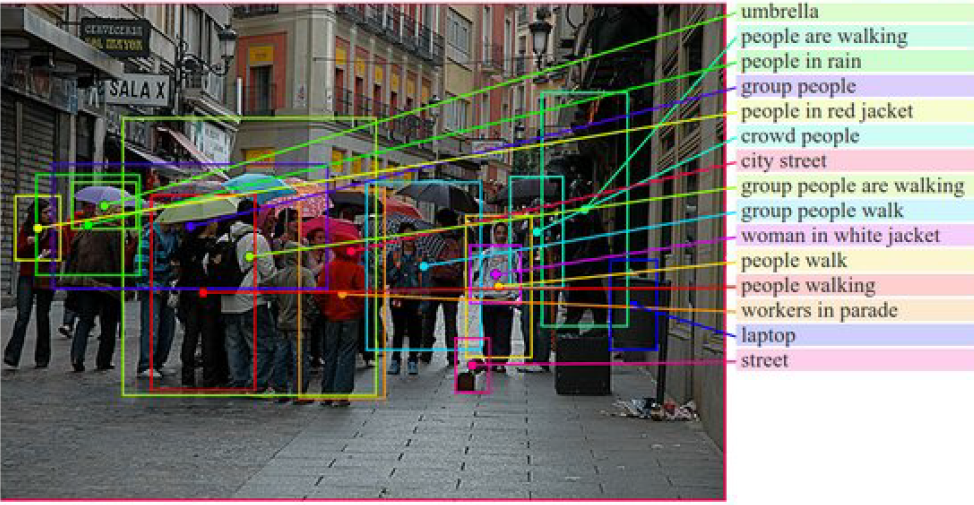
Approach
The project follows a progressive learning and implementation pipeline:
- Generative Extension: Leveraged the learned embeddings to train a caption generator that produces region-wise captions for unseen images.
- Theoretical Learning: Studied Neural Networks, CNNs, RNNs, and multimodal architectures.
- Region Proposal: Used Faster R-CNN for detecting regions of interest (bounding boxes).
- Feature Extraction (Visual Encoder): Implemented a VGG-19-based CNN to extract region-level features from each detected bounding box.
- Text Encoding (Language Encoder): Built an RNN/GRU-based model to convert textual captions into numerical embeddings.
- Multimodal Embedding Space: Mapped both image and text features into a shared vector space where similar image–text pairs lie close together.
- Alignment Training: Used a max-margin ranking loss to align image regions with corresponding caption fragments.
Dataset and Preprocessing
Source: Flickr30k Entities (an extension of Flickr8k/30k)
The Flickr30k dataset contains about 31,000 real-world images, each paired with 5 human-written English captions describing the scene.
Preprocessing Pipeline
1. Parsing
- Extracted image paths, captions, and bounding box coordinates from annotations.
2. Image Preprocessing
- Resized and padded images for uniform input size.
- Applied random cropping, rotation, and color jitter for data augmentation.
- Converted images to tensors normalized to the range [-1, 1].
3. Caption Preprocessing
- Tokenized sentences using
nltk. - Constructed a vocabulary with
<pad>,<start>,<end>,<unk>tokens. - Created word–index mappings and saved as
vocab.pkl.
4. Data Loader
- Returned paired (image, caption) tensors.
- Implemented
collate_fnto handle variable-length captions dynamically during batching.
Model Architecture
Alignment Model
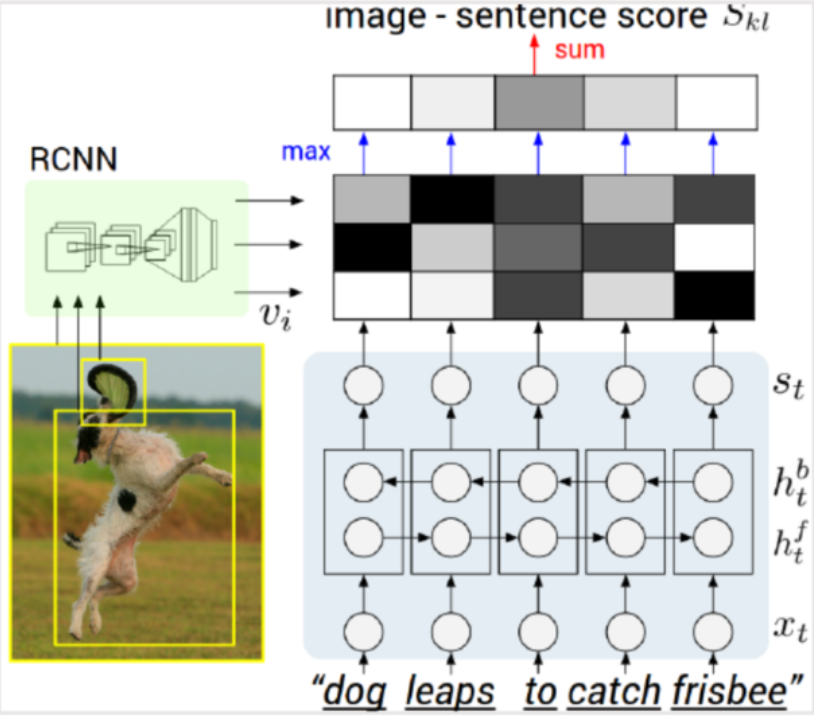
A. Encoder (AlignmentEncoderCNN)
- Based on VGG-19, pre-trained on ImageNet.
- Extracts deep region-level feature maps.
- Uses Adaptive Average Pooling (7×7) for uniform feature size.
- Passes pooled features through an FC layer → embedding vector.
- L2 normalization ensures fair similarity comparison with text vectors.
B. Decoder (AlignmentDecoderRNN)
- Uses Embedding + GRU + Linear layer.
- Encodes caption sequences into text embeddings.
- The final GRU hidden state represents the sentence meaning.
- Also L2-normalized for cosine similarity computation.
Intuitive Explanation
The alignment model learns a shared space where visually similar regions and semantically similar text lie close together. If a caption describes a region (e.g., “a brown dog”), their embeddings align closely in this space.
Mathematical Formulation
Image–Sentence Matching Score:
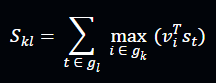
Where:
- vi: Image region vector
- st: Word or phrase vector
- Skl: Similarity between image k and sentence l
Loss Function (Max-Margin Ranking Loss):
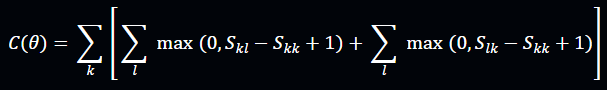
This ensures that correct image–caption pairs have higher similarity scores than mismatched ones.
Applications
| Domain | Application |
|---|---|
| Autonomous Systems | Scene understanding for perception & navigation |
| Medical Imaging | Describing localized anatomical regions |
| Surveillance | Detecting and describing activities in CCTV frames |
| Image Retrieval | Text-based search for image regions |
| Assistive Tech | Scene narration for visually impaired users |
Results

Team Members
- Aman Karki
- Ritika Varshney
- Nidhi Soni
Mentors
- Shaan Vora
- Rajas Daryapurkar
- Roushni Sareen
- Devansh Palan
- Sameh Nadeem